In the highly competitive world of business, customer satisfaction plays a pivotal role in determining the success and longevity of any company. Dissatisfied customers not only impact revenue and brand reputation but can also discourage potential customers from engaging with your products or services.
According to a survey (May 2022) by Statista, a favorable customer service experience increased respondents’ likelihood to make another purchase by 94%. In addition, 82% of customers said they would only recommend a business if it provided outstanding customer service.
This goes to tell how, as a customer service representative, it is crucial to understand how to identify dissatisfied customers proactively and take action accordingly.
How do you know if a customer is dissatisfied?
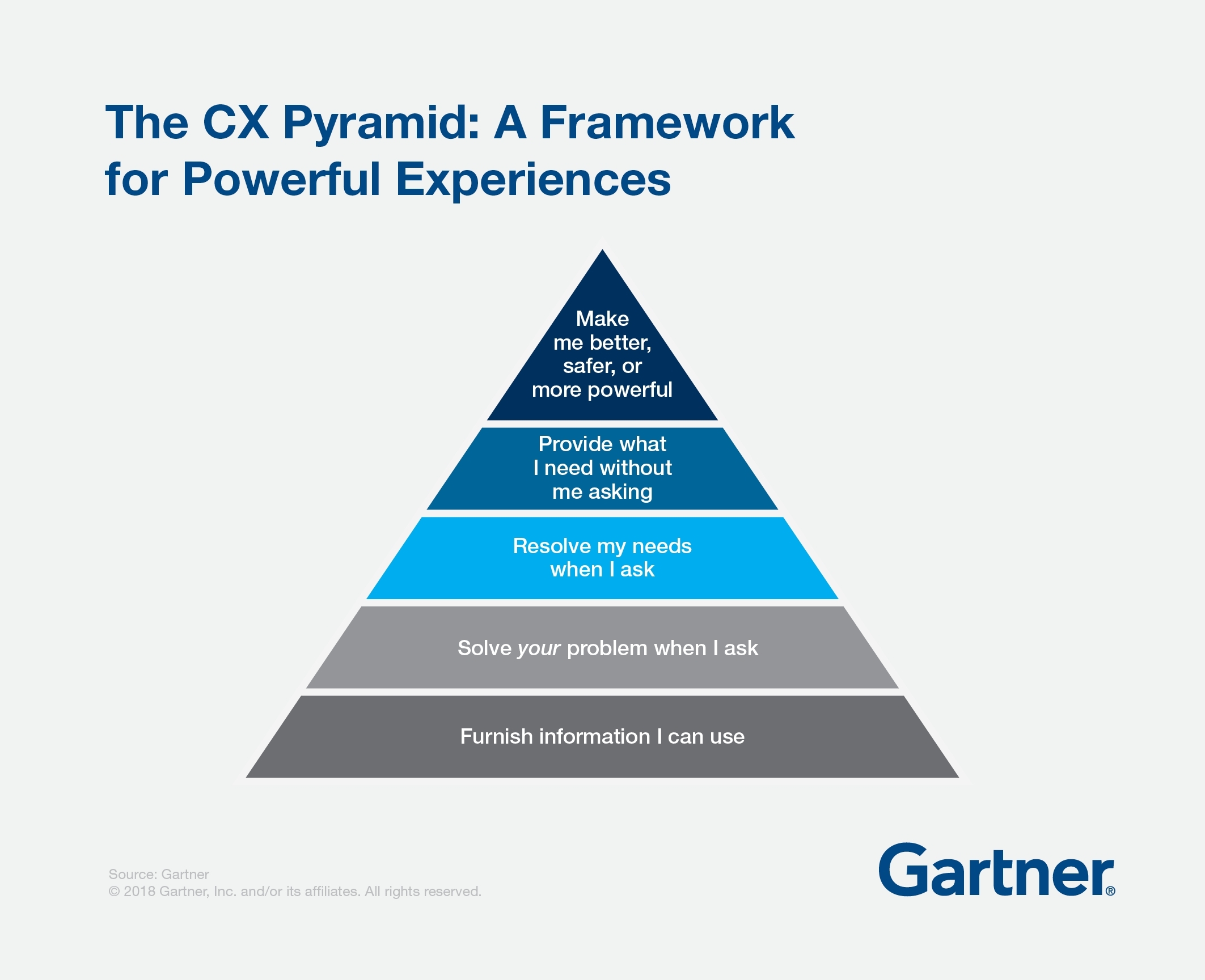
Source- Gartner
While 48 percent of CX leaders claim that their CX initiatives exceed management expectations, only 22 percent of CX leaders report that their CX efforts exceed customers’ expectations.
Hence, to understand customer dissatisfaction, testing customer journeys is extremely crucial.
The telltale signs of your customer dissatisfaction become extremely apparent after it crosses a certain threshold level. With satisfied customers comes revenue they also foster brand loyalty and advocacy. However, no business is immune to customer dissatisfaction, which can have detrimental effects on reputation and growth.
According to a study by Kolsky, 91% of customers who are unhappy with a brand leave for a competitor without even registering a complaint. Hence, even if a customer is making complaints, it might not mean that they’re unhappy with your services, and even if they are not complaining, it might mean they are going to churn soon because they no longer trust your services.
Let’s go through some of the key indicators that can help you identify when a customer is dissatisfied and resolutions to manage dissatisfied customers.
Excessive Complaints and Negative Feedback-
One of the most straightforward indicators of customer dissatisfaction is when customers voice their complaints or provide negative feedback. Whether it’s through direct communication, emails, or online reviews, customers will often express their dissatisfaction when they encounter issues with products, services, or the overall experience.
Make it a priority to actively listen to customer complaints and feedback. For responding promptly and empathetically, and showing that their concerns are acknowledged and taken seriously, an omnichannel CX dashboard is a must. Use this feedback to improve your offerings and prevent similar issues in the future.
Patterns of Customer Engagement-
A drop in customer engagement is a telltale sign of dissatisfaction. If customers are less active on your website, social media channels, email communications, or even on calls, it could indicate a waning interest in your brand.
Create engaging content and personalized experiences to keep customers interested and connected. Analyze customer behavior to understand their preferences better, enabling you to tailor your offerings to meet their needs.
Churn and Cancellation Rates-
High churn rates or an increase in customer cancellations are clear signs that something is amiss. When customers are dissatisfied, they are more likely to seek alternatives and switch to competitors.
Conduct exit surveys to understand the reasons behind customer churn. Use the insights gained to address pain points, enhance your products or services, and build stronger customer relationships.
Regular comparison with competition-
Always pay attention to what your customers are saying, especially when it comes to competitors. If your consumers are consistently bringing up the capabilities of your competitors and their capacity to offer what you cannot, this raises serious concerns.
The constant mention of your rivals indicates that either your service standards are subpar or your rapport with the client has deteriorated. You must carefully assess the needs of your clients and take appropriate action.
Net Promoter Score (NPS)-
Net Promoter Score (NPS) is a valuable metric for gauging customer loyalty and satisfaction. A low NPS score suggests a higher number of detractors (dissatisfied customers) within your customer base.
Regularly measure NPS and use the feedback to identify areas for improvement. Address the concerns of detractors while nurturing promoters to create brand advocates who will positively influence others.
Repeat Complaints-
When customers raise the same complaints repeatedly, it is a clear sign that they are dissatisfied with the lack of resolution or improvement.
Implement a robust feedback loop to capture and analyze customer complaints systematically. Identify recurring issues and take proactive steps to rectify them.
Types and examples of customer dissatisfaction
A survey conducted by Statista displays the proportion of customers in the United States and throughout the world who felt that the most annoying part of receiving subpar customer service was in 2018. One of the most upsetting aspects of a bad customer support experience, according to 18% of respondents to the survey, was not being able to address their problem on their own utilizing self-service.
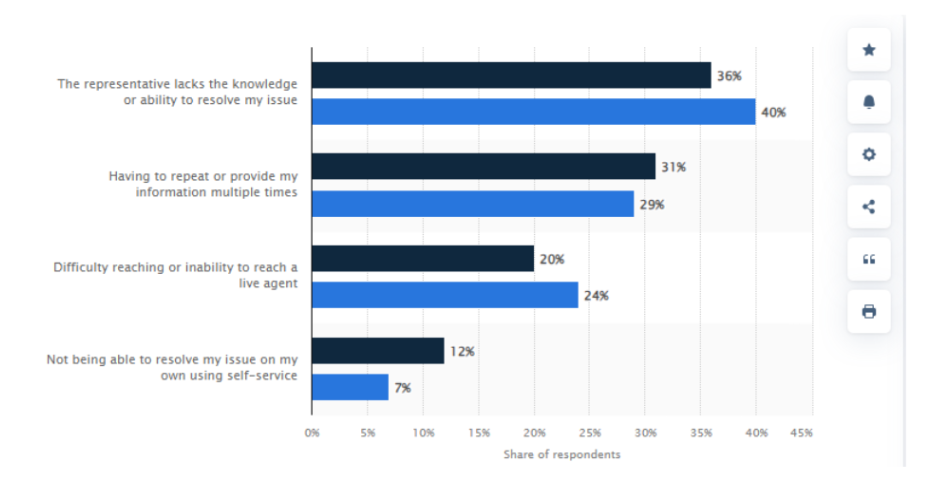
Source- Statista
It’s important for businesses to address customer dissatisfaction promptly and effectively, as unhappy customers can lead to negative reviews, reduced loyalty, and damage to the company’s reputation. By focusing on providing excellent customer experiences and listening to feedback, businesses can work towards improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Customer dissatisfaction can arise from various aspects of a product or service. Here are some examples of customer dissatisfaction:
- Product Quality: Customers may be dissatisfied if the product they receive does not meet their expectations in terms of quality, durability, or performance.
Example: A customer buys a new smartphone, but the camera doesn’t work properly, and the battery drains quickly.
- Poor Customer Service: Long waiting time, when a customer has to repeat his/her query multiple times to different service representatives can lead to dissatisfaction.
Example: A customer contacts a support helpline for assistance but is met with a rude and unhelpful representative who fails to resolve the issue.
- Hidden Fees or Charges: Customers may feel deceived if they encounter unexpected charges or fees when making a purchase.
Example- The advertised price for a room is $100 per night for the stay, which seems reasonable. The customer proceeds with the booking, assuming that the $100 covers the total cost. However, when received the credit card statement at the end of the month, the customer notices that they have been charged $150 per night for the stay.
- Lack of Communication: Customers expect clear and timely communication, and any lack of updates or information can be frustrating.
Example: A customer doesn’t receive any communication about the status of their order. Contacting the customer support helpline provided on the website, but no one answers their calls or emails. They feel dissatisfied with the lack of communication throughout the process and consider taking her business elsewhere in the future.
- Out-of-Stock Items: When a customer finds that the product they want to buy is out of stock, it can be disappointing.
Example: The customer visits their favorite retail clothing store to purchase a specific shirt their saw advertised in their latest collection. Upon arriving at the store, they search through the shelves but don’t find the shirt they want. They ask a store associate for assistance, and they inform them that the shirt they’re looking for is currently out of stock. In this example, the out-of-stock item leads to customer dissatisfaction. Customers may have specific preferences and expectations when they visit a store or shop online, and finding that a desired item is unavailable can be disappointing.
- Difficult Return or Refund Processes: Lengthy, complicated, or restrictive return or refund policies can result in customer dissatisfaction.
Example: A customer purchases a new smartphone online from an electronic store’s website. After receiving the phone, they realize that it’s not the model they intended to buy, and it lacks some essential features she specifically looked for in the product description.
Wanting to return the phone and get a refund, they navigate to the store’s website to find information about the return process. it states that returns are only accepted within 7 days of purchase, and the product must be in its original packaging with no signs of use. After completing the form and submitting the necessary documents, they wait for a response. However, the store takes several days to reply, further delaying the return process. In the meantime, they still need to use a phone that doesn’t meet their needs.
In this example, the difficult return or refund process creates a negative customer experience. The unclear return policy, unresponsive customer service, and cumbersome documentation requirements make it challenging for them to return the product and receive a refund promptly. Such experiences can leave customers feeling dissatisfied, and they may think twice about shopping with the store in the future.
- Lack of Personalization: Customers prefer personalized experiences, and when interactions feel generic or irrelevant, they may be dissatisfied.
Example: A customer receives marketing emails promoting products they have no interest in, indicating a lack of personalized targeting.
- Security and Privacy Concerns: If customers feel that their personal information is not adequately protected, it can lead to dissatisfaction and a loss of trust.
Example: Users may feel uneasy when their personal data is collected without clear consent. Complicated privacy policies can add to the confusion, leaving users unsure about the extent of data protection and control they have over their personal information. Such security and privacy concerns can affect user trust in the platform and its commitment to safeguarding their data.
- Poor Website or App Experience: A confusing or poorly designed website or mobile app can frustrate customers trying to make a purchase or find information.
Example: The poor website and app experience negatively impact the customers’ ability to browse and make a purchase. Slow loading times, cluttered layouts, broken links, and unresponsive app performance can frustrate users and drive them away from the platform. A poor online shopping experience can deter potential customers and result in lost sales and a negative perception of the brand’s digital presence.
- Long Wait Times: Lengthy wait times, whether in physical stores or for customer service support, can lead to dissatisfaction.
Example: A customer recently purchased a new laptop online, but when it arrived, they found that the screen had a dead pixel and the trackpad was not functioning correctly.
Concerned about the issues, they decide to contact the laptop manufacturer’s customer service helpline to resolve the problem. Frustration sets in as the wait time exceeds the initially estimated duration- 30 minutes. After 45 minutes of waiting on hold, a customer service representative finally answers their call.
While the representative is helpful and resolves the laptop issues, they can’t help but feel dissatisfied with the extensive wait time he had to endure. Having less AHT means a better CX.
Types of behavior customers show when a customer is dissatisfied
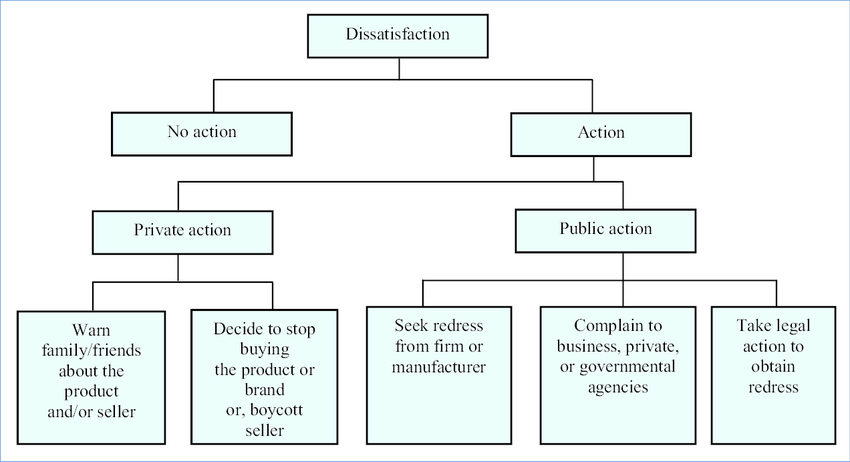
Understanding the different types of complaining customers can help businesses tailor their responses and resolution strategies accordingly.
Treating all customers with active listening, and genuine efforts to address their concerns can turn a complaining customer into a loyal and satisfied one. Complaining customers can be categorized into different types based on their behavior, communication style, and motivations for complaining. Here are the 5 most common types of complaining customers:
- The Assertive Complainer: This type of customer communicates their complaints clearly and confidently. They are not afraid to voice their dissatisfaction and expect a prompt resolution to their issues. Assertive complainers can be firm but generally remain respectful in their approach.
- The Aggressive Complainer: Aggressive complainers express their dissatisfaction with a more confrontational and hostile tone. They may raise their voice, use strong language, or make personal attacks during the complaint process. Dealing with aggressive complainers can be challenging, and it’s crucial to stay calm and professional while addressing their concerns.
- The Opportunistic Complainer: Opportunistic complainers use complaints as a means to gain some form of advantage, such as seeking discounts, refunds, or extra benefits. They may exaggerate issues to achieve their desired outcome. These can be easily handled through ML-backed chatbots using decision-tree algorithms.
- The Online Complainer: This type of customer takes their complaints to social media, online reviews, or forums. They use the power of the internet to amplify their concerns and potentially influence a larger audience.
- The Chronic Complainer: Chronic complainers are dissatisfied customers who continue to complain despite repeated efforts to resolve their issues. They may not be easily satisfied and might continue complaining even after their concerns have been addressed. Using customer-360, all their previous complaints can be easily seen on one interface and handled accordingly.
What do the dissatisfied customers want most?

Source- Shutterstock
Dissatisfied customers typically want specific outcomes or resolutions when they express their dissatisfaction. While individual customer needs and expectations may vary, some common things dissatisfied customers often want.
A little personalization goes a long way. Dissatisfied customers appreciate follow-up from the company after the resolution of their issue. They want to feel valued and appreciate the opportunity to provide feedback to help the company improve further.
Wrap-up
The one question that comes to mind while talking about customer dissatisfaction is, why care? Consider this- 13% of unsatisfied customers will tell 15 or more people when they’re disappointed with your brand.
A dissatisfied customer has a domino effect on others. Hence, even a single customer going discontented from your doors means a great deal for any business.
Talk to our product squad: schedule a demo today!
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,








