“Knowledge is ever-evolving, making knowledge management a never-ending effort.”
Competition in the SaaS industry, or any industry for that matter, is only getting tougher. When businesses embrace technology to stay competitive, one of the most promising technologies for successful end-user support is a knowledge management system.
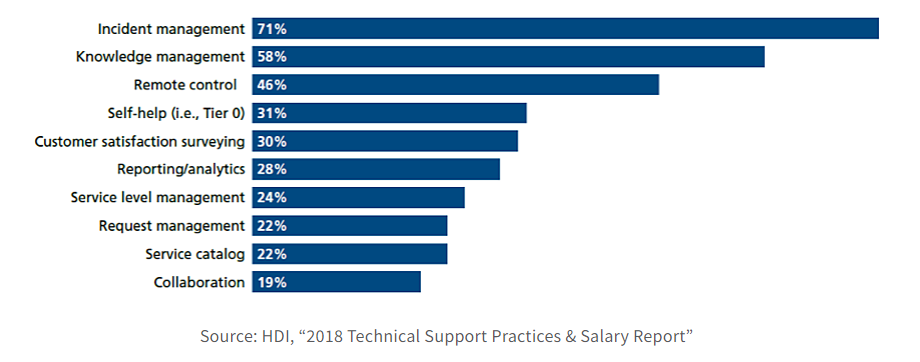
Knowledge management is a process that involves the development, curation, organization, and collective sharing of knowledge, including the efficient storage and retrieval of information for users.
When technology fails to meet user expectations and is not exploited to its full potential, it is considered a failure.
Read about the pinpointed reasons for the failure of a knowledge management system.
- Poor Goal Setting At Implementation Stage
- Lack Of Understanding Of Customer Needs
- Poor Content Organization
- Complex And Inferior Content Presentation
- Poor Structure Of Knowledge Base
- Storing Irrelevant Information
- Using Non-Scalable Knowledge Bases
- Non Approachability Of The Knowledge Base
- Lack Of End-To-End Collaboration
- Inadequate Feedback And Measuring Process
- Inaccessibility Across Mobile Devices
- Lack Of Personalized Content And Intelligent Software
- Lack Of A Dedicated Process And Team
- Lack Of Regular Updates
- Accessibility
Learn how to avoid knowledge management mistakes and how Kapture makes Knowledge Management successful.
1. Poor Goal Setting At Implementation Stage
The first step in creating anything is deciding what you want to achieve. Not recognizing how well a knowledge management system can benefit your organization can lead to ineffective implementation.
Find answers to your knowledge base’s purpose-related concerns. Will it, for example, satisfy both present and new customers? How should a knowledge base be set up to help employees and customers?
2. Lack Of Understanding Of Customer Needs
When you do not know what to include in your knowledge base, you may end up adding stuff that isn’t useful to your customers. They approach your knowledge base to get quick and appropriate answers to problems.
Step into the shoes of your customers and determine the quickest approach to focus on the information they desire.
3. Poor Content Organization
Anything that is organized is easy to maintain and locate.
If the content is not well-organized, customers may have to scan the article for a considerable period before zeroing in on the information that is necessary.
End-to-end information is pointless if it cannot provide customers with speedier assistance, and your knowledge base may end up scoring low on customer engagement levels.
When you give customers extensive paragraphs to read instead of quick resolutions, you are largely testing their patience and pushing them to look for better answers elsewhere.
4. Complex And Inferior Content Presentation
Simplicity is the ultimate sophistication. Keep the content in the knowledge base simple and handy.
Providing explanations merely in text format may not always help. When necessary, integrate GIFs, videos, screenshots, and flow diagrams to help with comprehension.
5. Poor Structure Of Knowledge Base
The absence of a proper structure in the knowledge base can be unprofessional. Provide a direction to the flow of information in the content as well as in the navigation bar. Give a logical path to the content by categorizing main topics into sub-topics.
For instance, if your product requires your user to renew a subscription and set up a payment to utilize it, you must include a link to the relevant payment guide in the “Renew subscription” knowledge base.
6. Storing Irrelevant Information
Do not consider the knowledge base as a dumping ground of all information. The main purpose behind setting up a knowledge base is to guide the customers to a solution without invoking external help. Keep well-curated and specific content that provides better resolution to queries.
7. Using Non-Scalable Knowledge Bases
Ideally, a knowledge base should expand alongside your organization to meet its knowledge support needs. Given the booming rate of data in the age of IoT, running your knowledge base in an on-premise system is a total misfire. Best alternative? Go for a cloud-based solution.
A cloud technology-based system takes care of data security and recovery too.
8. Non Approachability of The Knowledge Base
Making the knowledge base too hard to spot can take away all the fun out of it. When customers use your self-service option to access your knowledge base, they expect to find it quickly. They may seek answers elsewhere if they are unable to locate your knowledge base.
9. Lack Of End-To-End Collaboration
Organizations that lack a knowledge-sharing culture have a tough time deploying a knowledge management system. It’s because everyone, from experts to CEOs to service representatives is required to contribute to the knowledge base, and is certainly not somebody’s job. Hoarding knowledge is a big sin. Come out of it.
10. Inadequate Feedback and Measuring Process
While it is assumed that you collect timely feedback to measure the performance of your knowledge base, failing to act on it can be consequential.
The absence of precise metrics for monitoring the performance of the knowledge base does not help much with system improvement. For instance, when you intend to minimize the average resolution time get the feedback on those lines and see whether there is room for improvement.
11. Inaccessibility Across Mobile Devices
Support and service operations in an organization are restricted not just to office hours but round the clock. With remote work options, the users may have to access the knowledge base anytime and anywhere.
According to data from Google Analytics, “68.1% of all website visits in 2020 came from mobile devices—an increase from 63.3% in 2019.”
Consider whether your Knowledge Management software is light enough to load into mobile devices and has a design that adapts to small screens.
12. Lack Of Personalized Content And Intelligent Software
Anything that is not personalized can be likely doomed as uninteresting by customers. Personalization is indeed the one that keeps customers engaged.
According to Salesforce reports, ” By 2020, 51 percent of consumers will expect companies to anticipate their needs. Therefore, they will want the company to send them relevant content instead of doing the hard work of searching for themselves.”
See how knowledge management software may assist with content suggestion and discovery, contextual support, and viewing rights based on role.
13. Lack Of A Dedicated Process And Team
The absence of a defined process to look into the factors like specific access permission of knowledge base for customers and employees, ownership of content, approval methods, put things at stake.
Often, not having a dedicated team to look after the knowledge management system is a bottleneck. Anything that is not owned does not function to perfection.
14. Lack Of Regular Updates
Not bothering to update the knowledge base makes your content outdated and meaningless for the users and your Knowledge Management System ceases to fulfill its purpose. Neglected and outdated content is a turndown.
15. Accessibility
Even though you have all of the information in the knowledge base, users may be unable to access it. This can be due to poor keyword use that is not optimized for search engine discovery.
It is not just enough to identify the failure of the knowledge management system; prudence is also required to avoid knowledge management mistakes.
How to avoid knowledge management mistakes?
- When knowledge management systems directly impact the first call resolution rate, customer onboarding time, and average handling time, it is very important to establish clear-cut project goals before developing a knowledge base.
Make a list of the high-level objectives you hope to achieve by implementing a knowledge management system.
- Make it simple for customers to access your knowledge base, on your website and through search engines. Include links to the knowledge base in self-help features.
Source: Kapture
- Keep the content simple, comprehensible, complete, and latest.
- Run timed updates on your knowledge base. Revamp your content based on how your customers engage with your knowledge base, the most sought information, and so on.
Look into places for improvement, missing or redundant topics. Add new product details and remove old content that is no longer relevant.
- Instantly add new content from incoming support tickets that have just dealt with a new query resolution. This can be accomplished prospectively by prompting a take-action link to the knowledge base at case closure.
This allows you to expand your knowledge base alongside your organization.
- Have a protocol in place that outlines how to go about the knowledge management process, from identifying the required information to producing documentation, reviewing and approving the content.
Managers of individual departments can be granted the authority to approve content pertaining to their department.
- Set up autoresponders to collect real-time feedback so that you may act on the content as quickly as possible.
Knowing which articles were beneficial in delivering speedy solutions and which were not assists in identifying areas of improvement.
- Build a dedicated task force for the knowledge management process. Employ resources with the requisite skills to run the team with suggested roles as follows:
- Knowledge leaders or promoters of the knowledge management system
- Knowledge managers who acquire, administer, and validate the knowledge base.
- Writers and editors who capture documents and structure the content.
- Incorporate a measurement of parameters that aid in the improvement of the knowledge base’s practicability.
For instance measure content utilization and satisfaction, navigation time, and ease of access.
- Get powerful tools that may provide customized content recommendations based on customer interest and previous interactions with the platform.
Such solutions provide users with personalized content based on their role, ensuring that they do not see content that is irrelevant to them.
How does Kapture make Knowledge Management successful?
Kapture equipped with a modern and extensive knowledge base can constantly foster,
- Contextual and intelligent resolutions
- AI-powered assistance for a smooth customer experience
- Simple interfaces for smoother navigation
- Customizable bot workflows to cater to business requirements
- Powerful search engines for swift results
- Cross-platform accessibility
To take that confident and assured move ahead, your employee or customer requires the right knowledge base. Get started with Kapture. Learn more about the features by scheduling a free trial now.
About the Author | |
 | Seema C Mohan |
| Seema C Mohan is passionate about all things XaaS and loves to write value-added content. She has been in Business Process Management in the past and has published technology articles in journals. | |
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,