Customers trust a business when they choose to give them access to their personal data. In order to protect the privacy and security of the customer’s information, the business receiving it is responsible.
The reputation of the business is on the line if any user’s data falls into the wrong hands. In addition to risking its reputation, the corporation may have to shell out a sizable sum of money to defend itself from potential legal actions. Understanding PII compliance is crucial for keeping trust, safeguarding confidentiality, and avoiding legal ramifications whether you are a small business owner or a privacy-conscious individual.
What is PII Compliance?
Before understanding PII compliance, it is important to understand what is PII.
According to the most basic definition, it is any piece of information that can be utilized to determine a certain individual.
Names, email addresses, phone numbers, and addresses are a few types of PII.
Now coming to compliance, the term “PII compliance” refers to an accumulation of rules, guidelines, and procedures that organizations must follow in order to safeguard the privacy and security of personally identifiable information (PII) about individuals that is gathered, stored, processed, or communicated.
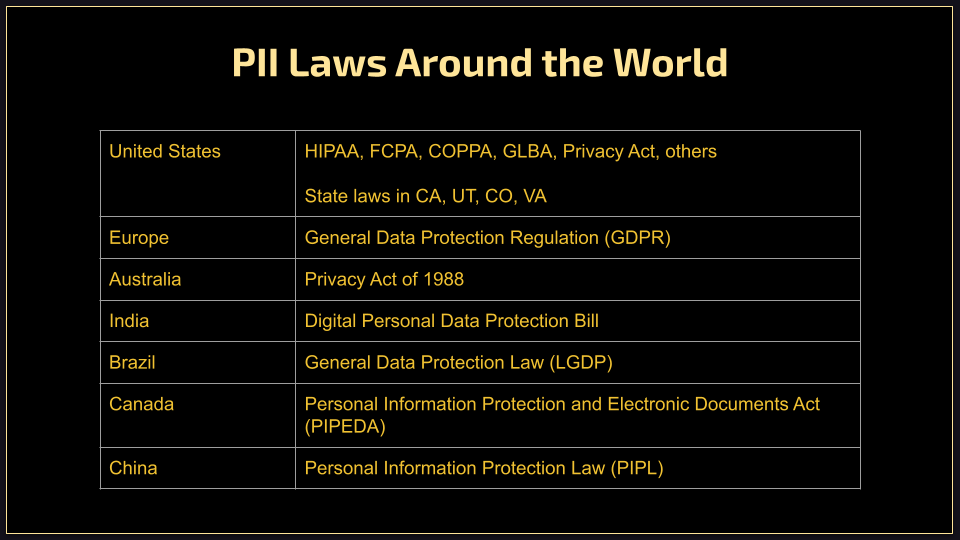
These are some of the examples of the main laws found around the world:
PII data classification: sensitive PII and non-sensitive PII
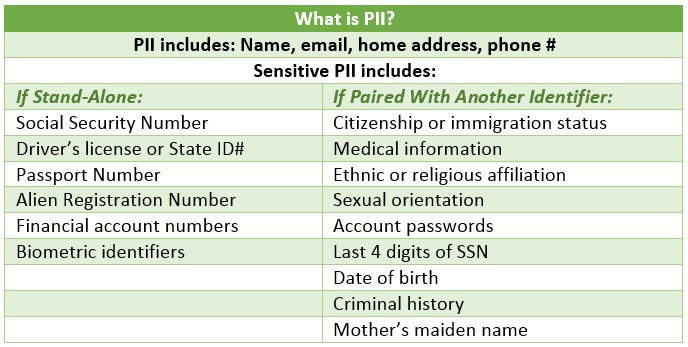
Although PII can be categorized in numerous ways, the majority of institutions and organizations adopt the broadest and most traditional distinction. PII is classified as sensitive and non-sensitive data.
Sensitive data is the kind of data that is not easily available in public records. It is the kind of information that would interest hackers and could be easily utilized for identity theft. Sensitive PII is data that, if revealed, might cause harm to the person if there is a data breach. For restricted disclosure of this kind of sensitive material, there are frequently legal, contractual, or ethical limitations.
Some examples of sensitive PII are:
- Social Security Numbers (SSNs)
- Passport Numbers
- Driver’s License Numbers
- National Identification Numbers
- Full Names Combined with Birthdates
- Financial Account Numbers
- Medical Record Numbers
- Health Insurance Information
- Biometric Data
- Employee ID Numbers
- Tax Identification Numbers
- Loan Application Information
- Social Media Account Credentials
- Birth Certificates and Marriage Certificates
Non-sensitive information must nevertheless be secured with the same strict standards as sensitive PII, while being readily accessible in public records like corporate directories, social media accounts, etc. The logic is simple.
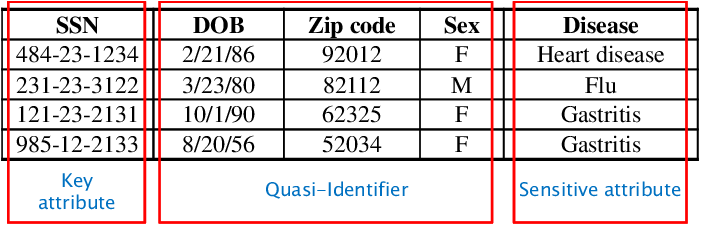
Everything here is a game of context. Although non-sensitive data fragments may be regarded as quasi-identifiers, when combined, they can easily act as sensitive data pieces. The email address, full names, and details about someone’s pets, date of birth, interests, etc., for instance, can be regarded as just quasi-identifiers and non-sensitive, but when combined, they can be quickly used to decipher someone’s social media passwords, making them sensitive PII.
Examples of non-sensitive PII:
- Basic Contact Information like first name, last name, phone numbers (non-private numbers), email addresses (non-personalized or non-sensitive), general demographic information
- Gender Job Titles
- Occupational information, such as job title or position
- Postal codes Educational Information
- School attended (without specific years)
- Field of study
- Social Media Handles
- Website Cookies
- General browsing behavior and preferences
- General interests (e.g., hobbies, favorite sports, books, movies)
- Public Posts and Comments
- Non-Personalized IP Addresses
How Can Businesses Stay Compliant with Privacy Laws?
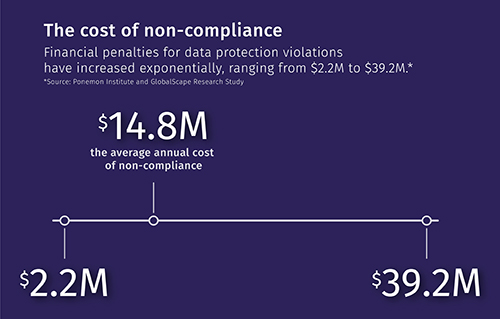
Staying compliant with privacy laws is crucial for businesses to protect the personal data of their customers and avoid legal and financial repercussions.
According to a study conducted by the research firm Ponemon Institute and the security provider GlobalScape, non-compliance costs businesses an average of $14.8 million annually. Financial penalties come with a hefty price tag that can range from $2.2 to $39.2 million; which is undoubtedly forcing organizations to change and make sure they are compliant.
Here are some steps businesses can take to ensure they maintain PII compliance:
1 . Identify the PII your company stores
Identify the various types of data your company collects and processes. This might include customer records, employee information, marketing databases, transaction logs, and more. Creating an inventory will be a valuable reference for identifying PII.
Document where the data comes from, and how it’s collected, stored, and used. Examine each data field in your inventory and assess whether it contains PII. Look for fields containing personal identifiers like names, addresses, phone numbers, email addresses, and other sensitive information.
2. Find all the places PII is stored
There are many ways through which you can find all the places where you can find all the PII stored in your company. One of them is by involving IT, data management, security, legal, and other relevant departments in this effort. A collaborative approach ensures that you cover all aspects of data storage.
Trace the flow of data through your organization. This involves understanding how data is collected, processed, shared, and stored at each step. If your company uses third-party services for data processing or storage, make sure to assess their data handling practices and their compliance with data protection regulations.
3. Classify PII in terms of sensitivity
Start by considering the potential harm or risk associated with each type of PII if it were to be exposed or misused. For instance, financial information could lead to financial fraud, while medical information could lead to health privacy violations.
Next, hop on identifiability and context. Information like full names and unique identification numbers (e.g., Social Security numbers) is highly identifying, while generic data like city names might be less so. Similarly, city name might not be sensitive, but when combined with SSN, it is sensitive-this is how context matters.
4. Give Customers Control Over Their PII
Giving customers control over their (PII) is a crucial aspect of respecting their privacy and complying with data protection regulations. Clearly communicate to customers what PII you collect, how it’s used, and why it’s necessary. Obtaining explicit, specific, unambiguous, and informed consent from customers before collecting and processing their PII goes a long way.
Remember that giving customers control over their PII isn’t just a regulatory requirement; it’s a fundamental aspect of building strong customer relationships based on trust and respect for their privacy.
5. Establish an acceptable usage policy
Establishing an Acceptable Usage Policy (AUP) for data compliance is crucial to ensure that your organization’s handling of data aligns with legal and regulatory requirements. It is important to clearly state the purpose and scope of the AUP for data compliance.
Specify the types of data and systems it covers, whether it’s customer data, employee data, sensitive financial information, or any other relevant categories. Outlining the procedures for reporting and responding to data breaches is the key to a perfect AUP. Include guidelines on notifying affected individuals, regulatory authorities, and other stakeholders as required by law.
6. Prevent Unauthorized PII Access
Unauthorized PII access can be prevented by implementing strong data security measures like:
- Encrypt sensitive data to protect it from unauthorized access.
- Establish access controls and restrict data access to authorized personnel only.
- Regularly update and patch software to address security vulnerabilities.
- Use firewalls and intrusion detection systems to safeguard networks.
7. Monitor Transactions Involving PII
While monitoring PII transactions is important, it must be done with a balance between security and respecting individual privacy.
Transparency with employees and stakeholders about monitoring practices can help maintain trust while safeguarding sensitive data. The first thing to do is to ensure that your monitoring practices align with legal requirements and ethical considerations to protect individuals’ privacy. It is also important to make sure that you continuously review your monitoring practices and tools to adapt to new threats and changes in data handling practices.
8. Delete PII when You’re finished with It
Deleting Personally Identifiable Information (PII) when it’s no longer needed is a fundamental principle of data protection and privacy.
Develop clear data retention policies that specify how long different types of PII will be kept. These policies should be based on legal requirements, business needs, and any industry-specific regulations. If you’re uncertain about the legal implications of data deletion, consult legal or compliance experts to ensure you’re following the appropriate practices.
9. Develop an employee education policy around the importance of protecting PII-
Whoever interacts with PII, be it sensitive or non-sensitive, should have certain etiquette to handle it. The primary objective of such a policy is to ensure that all employees understand the significance of protecting PII, comply with data protection regulations, and take proactive measures to prevent data breaches. An employee education policy should be communicated to all employees through written materials, training sessions, and internal communication channels.
PII compliance checklist
Cybercrime is growing exponentially. According to Cybersecurity Ventures, the cost of cybercrime is predicted to hit $8 trillion in 2023 and will grow to $10.5 trillion by 2025.
With data breaches at an all the time high, creating and implementing a PII compliance checklist goes a long way.
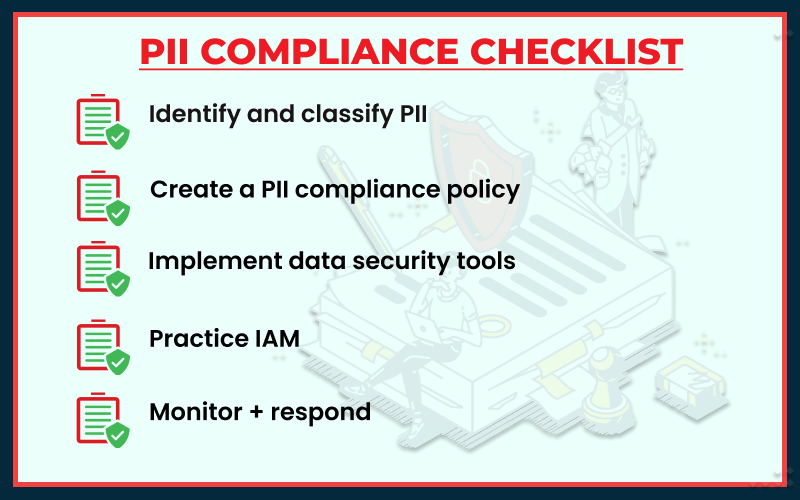
Step 1: Identify and classify PII:
The first step towards creating a PII compliance checklist is the identification and classification of the PII stored by any business. It is critical to research the applicable data protection and privacy laws and regulations in your jurisdiction. Different laws (such as GDPR, CCPA, HIPAA, and so on) may have different definitions of PII, and understanding these requirements will help you classify your data.
One of the most crucial components of a PII compliance checklist is creating a classification system for PII based on its sensitivity and risk. It could involve classifications like “Highly Sensitive,” “Moderately Sensitive,” and “Low Sensitivity.” For a thorough PII compliance check, constantly apply these labels to your data.
Step 2: Create a PII compliance policy:
Organizations handling sensitive personal data must have a Personally Identifiable Information (PII) compliance policy. A clear PII compliance policy lowers the risk of data breaches, guarantees legal and regulatory compliance, and helps safeguard people’s privacy.
Your organization’s unique demands and dangers should be taken into account while creating a PII compliance policy. Maintaining a proactive attitude towards data protection is crucial, along with continual training, communication, and development in your compliance efforts.
Step 3: Implement data security tools:
It is crucial to create a thorough implementation strategy including deadlines, resource allocation, and specified tasks. Think about how the tools will work with your current systems and procedures.
Select data security tools that meet the needs you have outlined. Encryption software, firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS), data loss prevention (DLP) options, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) tools are examples of common data security products. Make sure your data security tools adhere to industry standards and legal regulations. Conduct security audits on a regular basis to ensure compliance and pinpoint areas that need work.
Step 4: Practice IAM:
For adequate security and access control in an organization’s digital environment, identity and access management (IAM) practices are crucial. IAM assists in managing internal user identities, restricting internal staff members’ access to resources, and enforcing security regulations. The creation of explicit and thorough IAM policies that address user onboarding, access control, password management, data processing, and other topics is important.
Step 5: Monitor + respond:
A strong incident response plan must be in place, in the event that a breach occurs and the organization is alerted to it in time. As a result, PII and its security measures must be continuously monitored; any unauthorized access or acquisition must be quickly identified.
By doing this, an organization not only addresses and lessens the harm caused by the breach, but also starts the process of meeting any legal and regulatory requirements for data breach response.
Wrap-up
Customers are everything for any business. And every customer’s data is precious. When a customer decides to share confidential information with any company, it is the duty of it to not share it with anyone, be it on purpose or accidentally, both on moral and legal grounds. Hence, all companies must keep up with compliance best practices, emerging security threats, and updates to relevant regulations.
They should continuously assess data compliance processes, adapt to new challenges, and improve their security posture based on lessons learned.
Talk to our product squad: schedule a demo today!
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,








