Customer service is becoming a true growth engine for businesses across all industries.
Long waits on hold are no longer common. People now tag and message a brand on social media or even ask an AI assistant for help. No matter where the interaction happens, the expectation is the same: fast and consistent care. Miss the mark, and you risk losing not just a customer but their trust. Get it right, and even a small exchange can turn into a lasting relationship.
This blog takes a closer look at what customer support really means today, the channels people prefer, the tools businesses rely on, and the trends shaping the road ahead.
What Is Customer Support? Definition and Scope
Customer support is the direct link between a business and its customers when concerns or problems arise. Fundamentally, it ensures that customers receive help when they need it. But in practice, it is much more than a problem-solving desk.
Customer support is often confused with customer service, but there’s a key difference. Customer service refers to the broader relationship and overall experience a brand delivers across the customer journey, while customer support is the specific function focused on resolving issues, answering questions, and helping customers get the most out of a product or service. In short, service is the big picture, while support is the frontline of problem-solving.
Watch this quick explainer video to better understand customer support in action
With that distinction clear, customer support can be seen as the part of the business that reassures customers, keeps them informed, and guides them toward the best use of a product or service.
Strong customer support rests on a few essentials. Customers want clear answers without delays. They value conversations that feel respectful and personal rather than scripted. They also expect support to be available where they already are, whether that’s on the phone or in a chat window.
Scope of Customer Support
The scope of customer support goes beyond fixing problems—it covers every interaction that helps customers succeed, stay loyal, and feel confident in a brand. As expectations grow, the responsibilities of a customer support function continue to expand. Some of the most important areas include:
- Customer Onboarding: Providing resources that facilitate the experience of new clients and assisting them in understanding how to get started.
- Problem Handling: Resolving issues with products or services promptly and ascertaining that the remedy works the first time.
- Retention: Establishing trust that encourages enduring relationships and following up after a problem has been resolved.
- Insight Generation: Converting frequent support queries into input that can guide policy modifications or product design.
- Proactive Outreach: Foreseeing issues and providing answers before clients even inquire, such as about outages or usage tips.
- Stable Support: Ensuring that clients receive the same level of service across all platforms.
Types of Customer Support in 2026: From Technical to Proactive Care
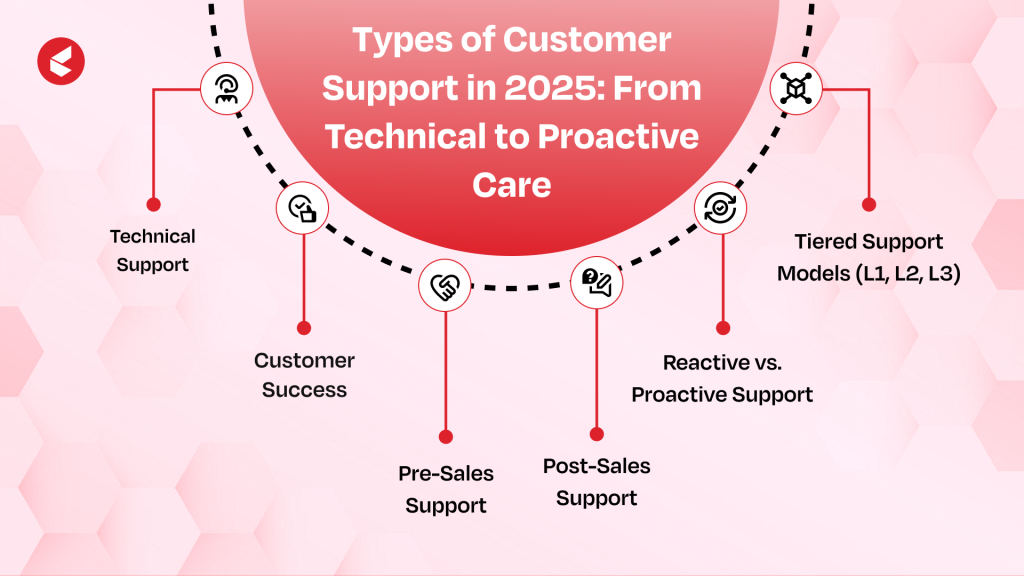
Customer support today is not a single department but a spectrum of roles that touch every stage of the customer journey.
Here is a breakdown of the major types of customer support:
1. Technical Support
Think of the last time a software update crashed mid-presentation. This is where technical support steps in. Often staffed by engineers or trained specialists, tech support handles error resolution, system downtime, product malfunctions, etc. Apple’s Genius Bar is a classic example of excellent tech support where customers get direct, hands-on help.
2. Customer Success
Unlike traditional support, customer success isn’t reactive at all. Its role is to make sure clients achieve the outcomes they signed up for. A SaaS company, for instance, may assign a dedicated success manager who checks in quarterly to make sure the client’s teams are actually using the platform to its full value.
3. Pre-Sales Support
Here, support operates almost like a bridge between sales and service. Before making a purchase, buyers frequently have technical inquiries. Pre-sales support alleviates doubt and resolves issues that can cause decision-making to stall. It builds trust and guarantees that potential customers believe the product will actually satisfy their needs.
4. Post-Sales Support
After the purchase, customers expect brands to stand by their product. A consumer electronics brand might offer instant warranty registration via QR code and doorstep pickup for faulty devices. The emphasis here is on turning a potential pain point into a loyalty-building moment. Brands can generate secure, branded codes with the QR Code Generator by Uniqode to streamline self-service and returns, a simple addition that aids and abets faster resolutions while strengthening customer trust.
5. Reactive vs. Proactive Support
Reactive support is familiar, waiting for a complaint and responding quickly. Proactive support flips this by anticipating issues. Airlines are a great example. Instead of passengers discovering delays at the gate, they receive instant rebooking notifications on their phones, along with meal vouchers, before they even ask.
6. Tiered Support Models (L1, L2, L3)
Tiered models balance efficiency with expertise. At Level 1, agents handle FAQs and basic fixes through chatbots or frontline staff. Level 2 involves subject-matter experts handling more complex cases. Level 3 is deep-dive engineering for systemic issues.
For example, an e-commerce company facing a payment gateway failure would move from L1’s script checks to L2’s transaction tracing and finally to L3’s engineering fix rolled out across all systems.
Why Customer Support Matters: Key Statistics and Impact
Behind every great brand is a support experience that keeps customers coming back. Get it wrong, and even one slip can cost you business. The numbers speak for themselves:
- 59% customers will leave a brand after just one bad interaction. (PwC)
- Around 13% of unhappy customers will go on to share their bad experience with 15 or more people. (American Express)
- Brands that listen win; 77% of consumers view them more favourably when they act on feedback. (Microsoft)
- 58% of customers say they’d never return after a poor service experience. (PR Newswire)
- Companies that deliver exceptional customer experiences see growth rates 4–8% higher than the market average. (Bain & Company)
- More than half of millennials (54%) are willing to pay extra for brands that deliver exceptional customer service. (Microsoft)
Top 10 Core Types of Customer Support Channels
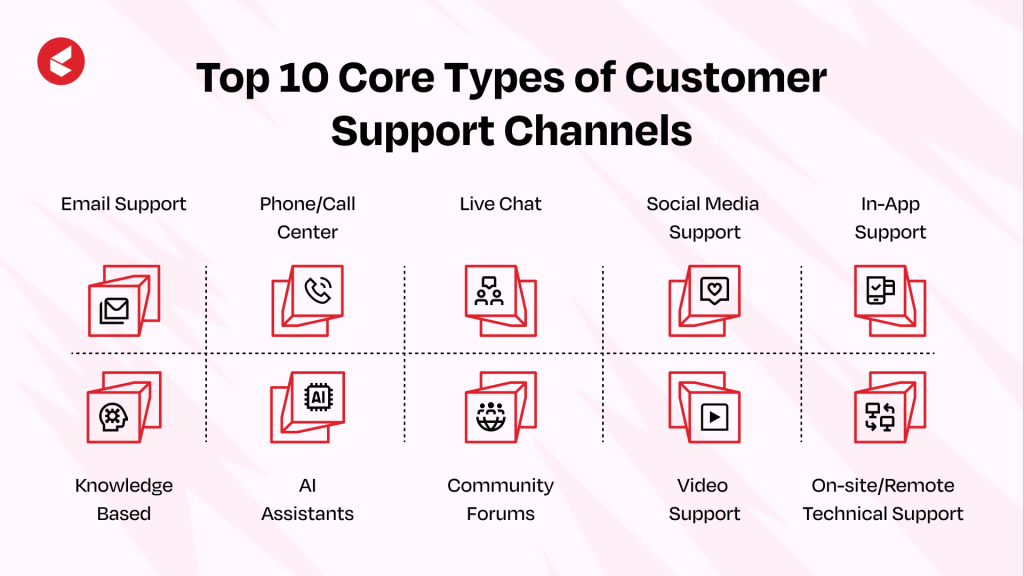
Customers expect you to meet them on their preferred channel and keep the conversation flowing. A connected CX system helps make that handoff smooth and consistent.
Keeping that in mind, here are the ten most critical customer support channels:
1. Email Support
Email remains one of the most trusted support channels. It is ideal for handling detailed queries and documentation-heavy issues. A good CX platform integrates email into ticketing systems, so that no request is ever lost.
2. Phone/Call Center
For urgent issues, phone support provides human reassurance and resolution speed. Call centers integrated with CX platforms allow real-time tracking of call logs and escalation paths, ensuring consistency across other channels.
3. Live Chat
Live chat offers instant, real-time assistance while customers are browsing. When integrated into CX systems, transcripts are stored for context and help agents to follow up easily if the issue escalates to another channel.
4. Social Media Support
Customers often reach out via different social media platforms for quick responses. Integrated CX solutions centralize social interactions with other support channels to prevent fragmented experiences. This helps brands keep a consistent tone and resolution.
5. In-App Support
Contextual assistance for SaaS and mobile-first enterprises is provided by in-app support. Guided tutorials, chat widgets, and embedded FAQs all improve user adoption. The app’s ability to provide instant assistance makes it one of the best methods for customer care.
6. Knowledge Base
Customers can use a knowledge base to solve problems on their own, which relieves support staff of some of their workload. It also shows which articles people use most, highlights what’s missing, and helps improve self-service by tracking how many tickets get avoided.
7. AI Assistants
AI-powered chatbots handle repetitive queries at scale and can route complex issues to agents. When synced with CX platforms, bots share conversation history with agents, so that customers don’t repeat themselves.
8. Community Forums
Forums allow peer-to-peer problem-solving and build customer communities. Such discussions highlight recurring issues and help product teams to identify trends and proactively address concerns.
9. Video Support
Video calls and co-browsing let agents guide customers through technical or onboarding challenges. Connected to CX platforms, these sessions are logged with case histories for customized future support.
10. On-site/Remote Technical Support
Some industries (hardware, telecom, enterprise IT, etc.) still require physical technical assistance. This channel addresses issues that cannot be solved digitally. Skilled technicians and strong scheduling systems are critical for making this channel effective. Though less scalable, it remains indispensable in high-stakes service environments.
Six Pillars of Effective Customer Support
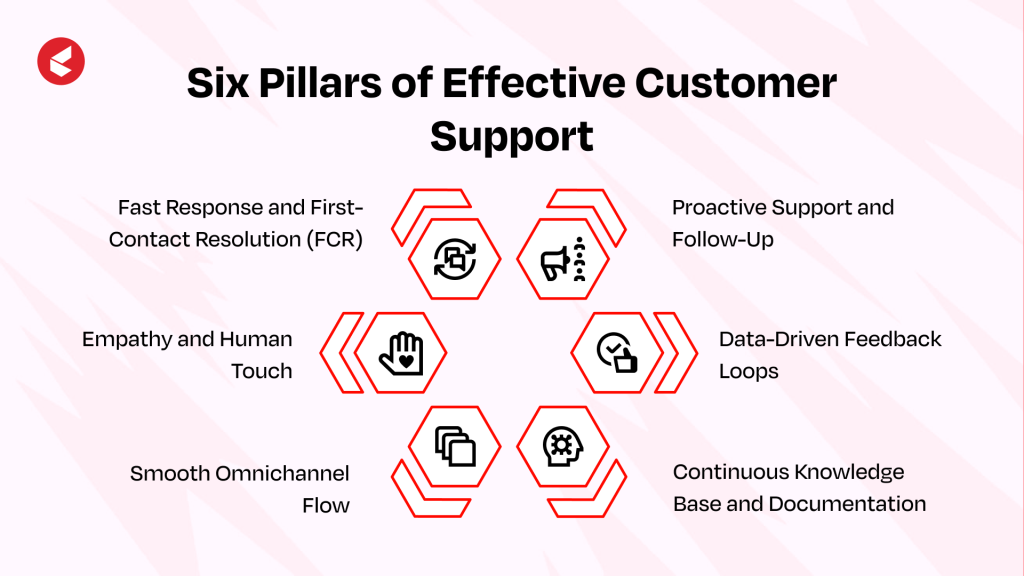
The first step in exceeding your customer’s expectations is to know those expectations. – Roy H. Williams
Effective customer support is built on six core pillars that ensure every interaction is faster, smoother, and more meaningful. These pillars act as the foundation for delivering consistent, trust-driven service.
The six pillars of effective customer service are as follows:
- Fast Response and First-Contact Resolution (FCR): When someone reaches out, their main hope is simple: “I don’t want to call again for the same problem.” That’s what FCR really measures. As per the Service Quality Management group, companies that hover around the 70–75% FCR mark usually see fewer repeat tickets and much higher customer trust.
- Empathy and Human Touch: Automation saves time, but it cannot replace the feeling that a real person actually cares. Even a short, empathetic response often diffuses frustration better than a long, robotic script.
- Smooth Omnichannel Flow: Jumping from email to chat or phone shouldn’t feel like starting over. Instead of six separate channels, a robust support system makes all of them part of the same discourse.
- Proactive Support and Follow-Up: Support doesn’t end once the ticket is closed. Checking in, offering updates before the customer asks, or even flagging issues early shows you are invested.
- Data-Driven Feedback Loops: Metrics such as net promoter score and customer satisfaction score serve as learning tools. The real value is in spotting patterns and making small but continuous improvements.
- Continuous Knowledge Base and Documentation: A living knowledge base serves as a shared memory for the team and customers alike. If it’s neglected, self-service becomes frustrating; if it’s cared for, it’s often the first line of real support.
Best Customer Support Tools for Every Support Type in 2026
When exploring what customer support requires in practice, the right tools make a huge difference. No single platform can do it all, so it’s important to match tools to specific support needs. Below are the major categories, with some of the best-fit platforms that continue to shape customer support.
1. Technical Support
As we have already covered, technical support deals with troubleshooting, product bugs, and system failures. This type of support depends heavily on ticket routing and quick escalation. Best tools to use for technical support include:
Freshdesk
- Use Case: Ideal for mid to large IT teams
- Standout Features: Robust ticketing, SLA management, agent collision detection
- Why It Stands Out: Its automation for repetitive tasks makes complex issue resolution faster.
- User Sentiment: “Easy to set up, efficient for IT support”
Zoho Desk
- Use Case: SMBs needing technical query handling
- Standout Features: AI reply suggestions, ticket tagging, and multichannel support
- Why It Stands Out: Context-aware responses that make technical troubleshooting less painful.
- User Sentiment: “Reliable, smooth, value for money”
2. Live Chat and Real-Time Support
Live chat provides immediate assistance, which is great for pre-sales queries and quick clarifications. Customers prefer this channel when they want ‘quick and human’ answers. Best platforms to use for live chat:
Intercom
- Use Case: B2C businesses with high daily inquiries
- Standout Features: Real-time messaging, proactive nudges, customizable chatbots
- Why It Stands Out: Balances AI-driven speed with the option for smooth human handoff.
- User Sentiment: “Feels modern and customer-friendly”
Drift
- Use Case: B2B companies for lead qualification and support
- Standout Features: Conversational AI and meeting scheduling
- Why It Stands Out: Turns customer support into a revenue-driving interaction.
- User Sentiment: “Cuts down response time and drives qualified leads”
3. AI Agents and Chatbots
AI-powered chatbots and virtual agents can handle all the transactional queries and even escalate to humans when needed. This type is critical for scaling support without ballooning costs. Best agentic AI platforms for customer service include:
Kapture CX
- Use Case: High-volume businesses that require scalable automation
- Standout Features: AI-backed self-service, smart routing, smooth CRM integration
- Why It Stands Out: Helps brands deflect repetitive queries while empowering agents to step in for nuanced cases.
- User Sentiment: “Saves time for both customers and agents, and speeds up resolution.”
Tidio
- Use Case: Small eCommerce stores looking for a quick bot setup
- Standout Features: Shopify integration, product recommendations, abandoned cart reminders
- Why It Stands Out: Affordable entry point into AI support
- User Sentiment: “Great balance of simplicity and automation”
4. Omnichannel Support Platforms
Customers do not stick to one channel. Omnichannel support ensures conversations continue seamlessly across chat, voice, social media, and more, without forcing customers to repeat themselves. Best platforms for omnichannel support are as follows:
Zendesk
- Use Case: Enterprises and scaling businesses
- Standout Features: Unified inbox, channel switching, deep integrations
- Why It Stands Out: One of the most complete omnichannel experiences available.
- User Sentiment: “Feels like everything is finally in one place”
HubSpot Service Hub
- Use Case: Companies already using HubSpot for CRM/marketing
- Standout Features: Shared inbox, customer portals, automation
- Why It Stands Out: Makes support part of the bigger customer lifecycle
- User Sentiment: “Smoothly links our sales, marketing, and support.”
Comparison Table: Customer Support Platforms Side by Side
Customer support in 2026 should match the right tool to the right type of support. A help desk platform might excel at structured ticket management, while an AI-powered system shines at handling repetitive queries instantly.
What is changing fast is how these tools are blending automation with human judgment. The real edge for businesses lies not in having the ‘most’ tools, but in knowing which support type each tool serves best.
Below, we break down the top tools by category to help map the need to a solution more effectively:
| Support Type | Tool | Best For | Key Features | Why It Stands Out |
| Technical Support | Freshdesk | Mid to large IT teams | Ticketing, SLA management, and agent collision detection | Strong automation speeds up technical resolution |
| Zoho Desk | SMBs handling technical queries | AI replies, ticket tagging, multichannel support | Context-aware responses make troubleshooting smoother | |
| Live Chat & Real-Time Support | Intercom | B2C businesses with heavy daily inquiries | Real-time chat, proactive nudges, customizable bots | Blends AI speed with human handoff |
| Drift | B2B companies needing lead qualification | Conversational AI, meeting scheduling | Turns support into revenue-driving engagement | |
| AI Agents & Chatbots | Kapture CX | High-volume businesses | AI self-service, smart routing, multilingual, CRM integrations | Scales automation while keeping handover to agents smooth |
| Tidio | Small eCommerce stores | Shopify integration, product suggestions, cart reminders | Affordable way to add AI-driven support | |
| Omnichannel Support | Zendesk | Large enterprises and scaling firms | Unified inbox, channel switching, and wide integrations | Delivers one of the most complete omnichannel setups |
| HubSpot Service Hub | Companies using the HubSpot ecosystem | Shared inbox, portals, automation | Connects support with sales and marketing workflows |
How Does Customer Support Fit Into Overall CX Strategy?
Customer support is often thought of as a standalone function, but that’s not true. It directly shapes customer perception of the entire brand.
According to a McKinsey study, 76% of consumers become irate when businesses do not provide them with individualized customer service. In support conversations, that frustration frequently comes up.
On the other hand, businesses that excel at customizing customer service can see a 10–15% rise in revenue. This demonstrates the close relationship between customer experience and business expansion.
Customer support is also the clearest proof of whether a brand actually lives up to its promises. A customer might enjoy a slick website or a strong ad campaign, but if their issue is not resolved quickly when they reach out, the entire experience breaks down. A study by PwC found that one in three customers will walk away after a single bad interaction.
The other role support plays is as an insight engine. Tracking measures like CSAT scores or repeat issue rates surface recurring friction points. When these insights feed into product design or service processes, customer pain is reduced at the root level.
Simply put, customer support is the front line of customer experience. It’s the point where strategy either proves itself or falls apart.
Future Trends in Customer Support
Given below are some of the major trends that will revolutionize customer support in the coming years.
- AI will move beyond chatbots into decision intelligence, providing agents with real-time suggestions and context. (IBM)
- Voice assistants will gain traction as natural language models become more accurate and multilingual. (Master of Code)
- Hyper-personalization will replace generic responses, driven by unified customer profiles. (Forbes)
- Predictive analytics will anticipate issues before customers report them to reduce inbound volumes. Human agents will focus on emotional or high-value interactions as automation takes over routine cases. (IBM)
- Data privacy and ethical AI will become differentiators. (Startelelogic)
- Self-service will expand into video-driven tutorials and immersive experiences. (IBM)
Conclusion: Is Your Customer Support Ready for 2026?
Get closer than ever to your customers. So close that you tell them what they need well before they realize it themselves.
– Steve Jobs
Ultimately, understanding what customer support means today is about recognizing its role as both a trust-builder and a growth driver. Companies that treat support as a frontline source of intelligence and feed customer insights back into product design and operations gain a real competitive advantage.
If your current setup isn’t built for that level of intelligence and agility, it’s time to upgrade. Kapture CX equips businesses with tools to automate decisions and deliver customer support that’s ready for the future.
Contact us today to learn more!
FAQs
Customer support is the function that helps customers resolve issues, answer questions, and get the most value from a product or service. Unlike broader customer service, support focuses on problem-solving and direct assistance. It’s important because effective support builds trust, improves retention, and turns one-time buyers into long-term loyal customers.
A good experience often turns frustrated customers into loyal ones, and loyal customers tend to spend more and stay longer. That repeat business adds up, which is why support should be seen as a growth lever.
Every ticket or chat is feedback in disguise. When recurring issues are flagged back to product teams, it helps them prioritize fixes and new features that customers actually want.
If support runs in isolation, teams miss out on context. By linking it with CRM or sales data, agents can see the full customer journey. That makes interactions more personal and helps businesses predict future needs instead of always reacting.















5 thoughts on “What Is Customer Support? Top Channels, Tools and Trends Explained”
Comments are closed.